In late May 2025, Ars Technica reported the alarming story of a healthy man who went camping in Argentina and ended up in the ICU for 40 days with acute respiratory failure. Initially, he showed no symptoms, but days later developed shortness of breath, low oxygen saturation and shock hallmarks of cardiopulmonary hantavirus syndrome (HPS), a rare yet potentially fatal condition that typically develops within 1 to 8 weeks after inhaling airborne particles from rodent urine, droppings, or saliva.
Understanding HPS: Signs and Progression
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) often begins with flu-like symptoms:
- Fever, muscle aches, headache, fatigue
- Gastrointestinal issues: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Within 4 to 10 days, more severe respiratory symptoms emerge: dry cough, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and fluid accumulation in the lungs, often progressing rapidly to respiratory failure.
Globally, HPS carries a mortality rate of 30–60%, largely due to severe lung complications and shock.
Prevention in Wilderness Settings
No vaccine or specific antiviral treatment exists for HPS. Management is exclusively supportive (e.g., ventilation, cardiac support) and early detection is critical. To minimize risk while camping:
- Avoid areas with rodent droppings or nests
- Keep food sealed and dispose of waste properly
- Use gloves and masks when cleaning areas potentially contaminated by rodents
- Seal campsites against rodent entry and keep them clean
Monitoring Health: The Role of Temperature Checks
Early symptoms overlap with common illnesses, but fever is a key trigger to seek medical attention, especially when paired with respiratory signs. Checking one’s body temperature twice daily, morning and evening, can help detect a fever early.
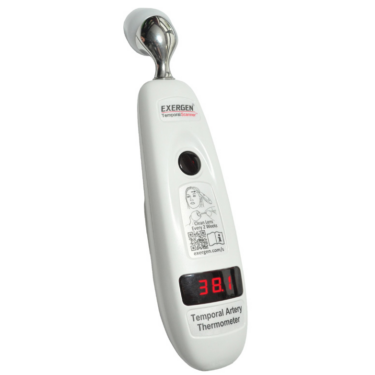
An easy‑to‑use, reliable, and accurate thermometer like the Exergen Temporal Artery Thermometer is ideal for this purpose. Temporal artery thermometers measure infrared heat from the forehead, providing quick, non‑invasive readings that closely reflect core body temperature
Why Choose a Temporal Artery Thermometer?
- Provides rapid, non‑invasive readings; no probes or ear inserts needed.
- Backed by over 100 peer‑reviewed clinical studies, including hospital and home use across all ages.
- Employs Exergen’s Arterial Heat Balance method, ensuring high accuracy, unlike cheaper non-contact infrared devices.
Recommended Models for Twice‑Daily Monitoring
Here are reliable temporal artery thermometers suitable for regular use at home or in the field:
- Exergen TAT‑2000C TemporalScanner: Designed for clinical settings, featuring Exergen’s patented AHB method and over 100 supporting studies
- Ideal for those wanting hospital-level precision.
- Exergen ComfortScanner Temporal Thermometer: A more affordable but still accurate option for home and travel use, rated highly by users.
- Exergen TempoTherm: an extremely easy to use consumer-grade Temporal Artery Thermometer available in countries like Europe.
The case of the healthy camper hospitalized in Argentina shows that even low-risk outdoor trips can swiftly escalate into serious illness. With no specific treatment for HPS, early detection is essential. Checking your temperature twice daily using a trusted thermometer like Exergen’s Temporal Artery Thermometer is a practical, proactive measure. It can alert you to fever early, prompting timely medical evaluation and possibly improving outcomes.
Stay safe and aware of your health, even in the wilderness.
Sources:
- Ars Technica: https://arstechnica.com/health/2025/05/healthy-man-goes-camping-lands-in-icu-for-40-days-with-respiratory-failure/
Exergen P/N 850469